Additional information
| Source area | Pomigliano/Brusciano countryside – Italy |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Intake | Vegetable with good content of potassium, phosphorous, magnesium, zinc, iron, selenium and sodium. The fresh vegetable is rich in glucose, sucrose and soluble fiber, vitamin A, B6, E, J, K1 carotenoids like β-carotene, capsanthin, capsorubin, lutein and zeaxanthin. Among the antioxidants, we have a good amount of polyphenols like ellagic acid. Capsaicin (1,5% weight) gives spiciness to its seeds. |
| Period of transformation | From the second week of August to the third week of September |
| Trivia | The ethymological development of this pepper’s name derives from vulgar Latin: “pipiricella” (little pepper)> paparicella>paparcella>papacella, up to the current name “papaccella”. Each color means a different taste: GREEN: green peppers are less mature and rich in chlorophyll, magnesium, pectin and polysaccharides which nourish and support the plant. RED: antocyanic concentrations and lycopene give this bright color to the vegetable, full of antioxidant properties. YELLOW: rich in carotenoids, phyto-colorants and antioxidants. |
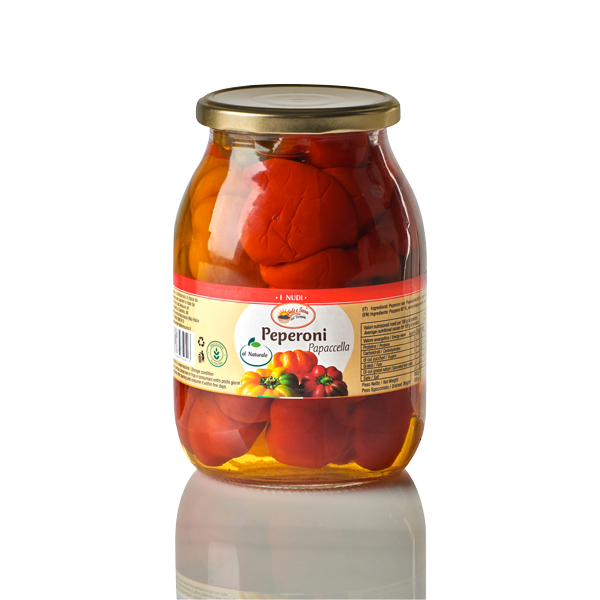





 Neapolitan Curly Pepper 60%
Neapolitan Curly Pepper 60% Wine vinegar
Wine vinegar Water
Water Sea salt
Sea salt Acidifier: citric acid – Antioxidant ascorbic acid.
Acidifier: citric acid – Antioxidant ascorbic acid.



